 快速开始
快速开始
提示
如果您用过Mybatis-Plus的话,您基本上可以无需多看此文档即可直接上手使用 Easy-Es是Mybatis-Plus在Elastic Search的平替版.
我们将通过一个简单的 Demo 来阐述 Easy-Es 的强大功能,在此之前,我们假设您已经:
- 拥有 Java 开发环境以及相应 IDE
- 熟悉MySQL
- 熟悉 Spring Boot (推荐版本2.7.x +)
- 熟悉 Maven
- 了解Es基本概念或已读避坑指南 (强烈推荐)
- 已安装Es 推荐7.x版本(没有安装的可自行百度教程,建议再装一个es-head插件,便于可视化验证),低版本可能存在API不兼容或其它未知情况,因为底层采用RestHighLevelClient而非RestLowLevelClient,本Demo采用Es版本为7.17.8
推荐
推荐您参考这篇Springboot集成demo,可帮助您节省您更多时间.
特别注意
由于springboot内置关联了es版本,不同的springboot版本会导致实际项目中引入的es依赖版本过低或过高, 而es不同版本兼容性比较差,很多用户踩到一些因依赖冲突而导致兼容问题的坑,在此特地提醒用户,如果您项目实际依赖的es版本不为 7.17.28版本,我们强烈建议您显示指定es依赖jar包版本为7.17.28,与我们底层使用的es依赖版本保持一致,如此兼容性最佳, 不易踩坑. 底层之所以采用7.17.28也是经过多方调研,选择了一个稳定无安全漏洞的版本,经墨菲扫描该版本安全可靠,并且可以向上兼容es8.x 至于ES客户端版本,7.x+实测兼容性都非常出色,依赖中的jar包版本与客户端版本不匹配无妨,重点是依赖的Jar版本.
# 初始化工程
创建一个空的 Spring Boot 工程
提示
可以使用 Spring Initializer (opens new window)快速初始化一个 Spring Boot 工程
# 添加依赖
Maven:
<!-- 引入easy-es最新版本的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.dromara.easy-es</groupId>
<artifactId>easy-es-boot-starter</artifactId>
<!--这里Latest Version是指最新版本的依赖,比如3.0.0,可以通过下面的图片获取-->
<version>${Latest Version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 如果有依赖冲突,导致底层es相关依赖非7.17.28,需要参考避坑指南章节文档先排除springboot中内置的es依赖-->
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Gradle:
compile group: 'org.dromara.easy-es', name: 'easy-es-boot-starter', version: 'Latest Version'
# ✨最新版本 Latest Version:  (opens new window)
(opens new window)
# 配置
在 application.yml 配置文件中添加EasyEs必须的相关配置:
easy-es:
compatible: true # 兼容模式开关,默认为false,若您的es客户端版本小于8.x,务必设置为true才可正常使用,8.x及以上则可忽略此项配置
enable: true #默认为true,若为false则认为不启用本框架
address : 127.0.0.1:9200 # es的连接地址,必须含端口 若为集群,则可以用逗号隔开 例如:127.0.0.1:9200,127.0.0.2:9200
username: elastic #若无 则可省略此行配置
password: WG7WVmuNMtM4GwNYkyWH #若无 则可省略此行配置
2
3
4
5
6
其它配置暂可省略,后面有章节详细介绍EasyEs的配置
在 Spring Boot 启动类中添加 @EsMapperScan 注解,扫描 Mapper 文件夹:
@SpringBootApplication
@EsMapperScan("com.xpc.easyes.sample.mapper")
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 背景
现有一张Document文档表,随着数据量膨胀,其查询效率已经无法满足产品需求,其表结构如下,我们打算将此表内容迁移至Es搜索引擎,提高查询效率
| id | title | content |
|---|---|---|
| 主键 | 标题 | 内容 |
# 编码
编写实体类Document.java(此处使用了 Lombok (opens new window)简化代码)
@Data
@IndexName
public class Document {
/**
* es中的唯一id
*/
private String id;
/**
* 文档标题
*/
private String title;
/**
* 文档内容
*/
private String content;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
温馨提示
- 上面字段名称以及下划线转自动驼峰,字段在ES中的存储类型,分词器等均可配置,在后续章节会有介绍.
- String类型默认会被EE创建为keyword类型,keyword类型支持精确查询等
- 如需分词查询,可像上面content一样,在字段上加上@IndexField注解并指明字段类型为text,并指定分词器.
编写Mapper类 DocumentMapper.java
public interface DocumentMapper extends BaseEsMapper<Document> {
}
2
# 前置操作
手动创建索引(相当于MySQL等数据库中的表),有了索引才能进行后续CRUD操作.
@Test
public void testCreateIndex() {
// 测试创建索引,框架会根据实体类及字段上加的自定义注解一键帮您生成索引 需确保索引托管模式处于manual手动挡(默认处于此模式),若为自动挡则会冲突
boolean success = documentMapper.createIndex();
Assertions.assertTrue(success);
}
2
3
4
5
6
温馨提示
- 我们目前提供了4种索引创建的方式,上述演示的是推荐新手使用的一键创建模式,如果您对其它集中模式感兴趣,可以移步至索引托管章节查看
- 其中自动挡模式之平滑模式可以自动感知索引变化,自动调整索引,平滑迁移数据,但不推荐小白使用,建议了解原理及源码后再使用
- 当然您也可以通过其它几种模式来维护索引,或者通过logstash,es-head等工具进行索引维护
# 开始使用(CRUD)
添加测试类,进行功能测试:
测试新增: 新增一条数据(相当于MySQL中的Insert操作)
@Test
public void testInsert() {
// 测试插入数据
Document document = new Document();
document.setTitle("老汉");
document.setContent("推*技术过硬");
int successCount = documentMapper.insert(document);
System.out.println(successCount);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
测试查询:根据条件查询指定数据(相当于MySQL中的Select操作)
@Test
public void testSelect() {
// 测试查询 写法和MP一样 可以用链式,也可以非链式 根据使用习惯灵活选择即可
String title = "老汉";
Document document = EsWrappers.lambdaChainQuery(documentMapper)
.eq(Document::getTitle, title)
.one();
System.out.println(document);
Assert.assertEquals(title,document.getTitle());
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
测试更新:更新数据(相当于MySQL中的Update操作)
@Test
public void testUpdate() {
// 测试更新 更新有两种情况 分别演示如下:
// case1: 已知id, 根据id更新 (为了演示方便,此id是从上一步查询中复制过来的,实际业务可以自行查询)
String id = "krkvN30BUP1SGucenZQ9";
String title1 = "隔壁老王";
Document document1 = new Document();
document1.setId(id);
document1.setTitle(title1);
documentMapper.updateById(document1);
// case2: id未知, 根据条件更新
LambdaEsUpdateWrapper<Document> wrapper = new LambdaEsUpdateWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq(Document::getTitle,title1);
Document document2 = new Document();
document2.setTitle("隔壁老李");
document2.setContent("推*技术过软");
documentMapper.update(document2,wrapper);
// 关于case2 还有另一种省略实体的简单写法,这里不演示,后面章节有介绍,语法与MP一致
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
经过一顿猛如虎的更新操作 我们来看看标题最终变成了什么?
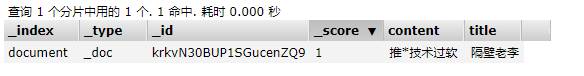
查询结果证实了我们更新没有问题,这里无意冒犯"老李",仅供演示,如有得罪,请海涵.
测试删除:删除数据(相当于MySQL中的Delete操作)
@Test
public void testDelete() {
// 测试删除数据 删除有两种情况:根据id删或根据条件删
// 鉴于根据id删过于简单,这里仅演示根据条件删,以老李的名义删,让老李心理平衡些
LambdaEsQueryWrapper<Document> wrapper = new LambdaEsQueryWrapper<>();
String title = "隔壁老李";
wrapper.eq(Document::getTitle,title);
int successCount = documentMapper.delete(wrapper);
System.out.println(successCount);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
提示
上面完整的代码示例请移步:Easy-Es-Sample (opens new window)
# 小结
通过以上几个简单的步骤,我们就实现了 Document的索引创建及CRUD 功能,最终也帮老李洗白了. 从以上步骤中,我们可以看到集成Easy-Es非常的简单,只需要引入 starter 工程,并配置 mapper 扫描路径即可。 但Easy-Es 的强大远不止这些功能,想要详细了解 Easy-Es 的强大功能?那就继续往下看吧!
